Magento, known officially as Adobe Commerce for several years now, remains a powerhouse in the ecommerce sector. While new platforms pop up regularly, major brands and enterprise-level retailers continue to rely on Magento because of its unparalleled flexibility and robust catalog management capabilities. However, as we settle into 2026, the way we approach Ecommerce SEO for this platform has shifted. It is no longer just about keywords and backlinks. Today, successful Magento SEO requires a sophisticated blend of technical infrastructure, entity optimization for AI search engines, and a relentless focus on user experience metrics.
For SEO specialists and store owners, Magento presents a unique paradox. Out of the box, it is arguably one of the most SEO-friendly platforms available regarding architecture, yet it is also one of the easiest to break if you do not know what you are doing. A default installation often suffers from duplicate content issues, slow load times due to heavy JavaScript, and complex URL structures that can confuse crawlers.
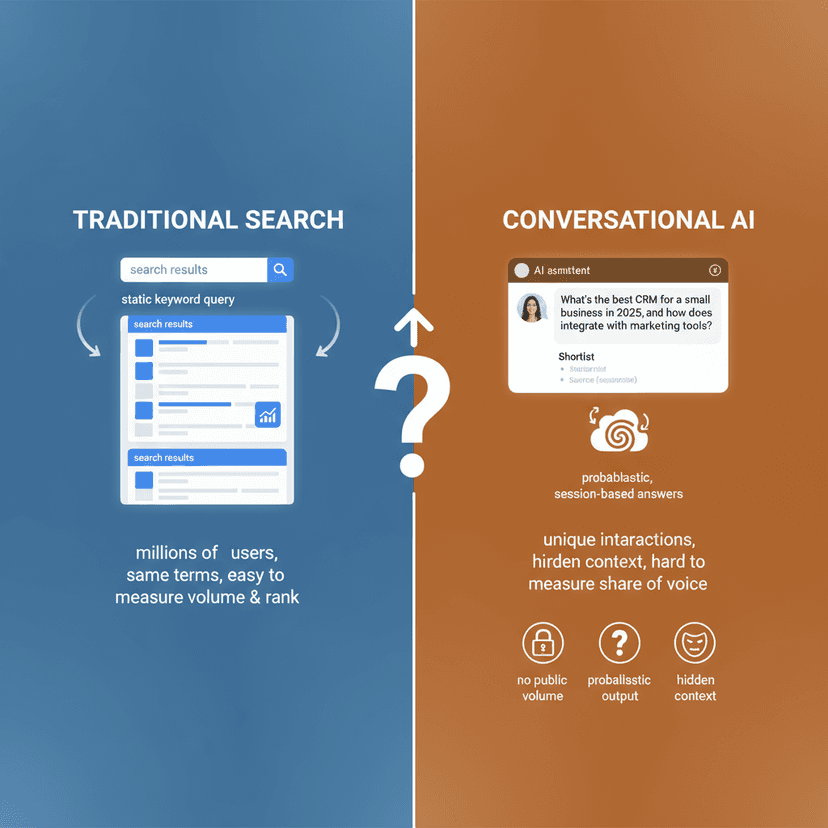
The stakes are higher now than they were five years ago. Search engines have evolved into answer engines. With the rise of AI-driven search experiences, such as Google’s AI Overviews and various agentic search tools, your store needs to be optimized for machines that read and understand data like humans do. This guide dives deep into the specific challenges and opportunities within the Adobe Commerce ecosystem, providing a roadmap to secure organic visibility in a highly intelligent search environment.
The Technical Foundation: Speed and Core Web Vitals
In 2026, site speed is not merely a tie-breaker; it is a fundamental requirement for indexation and ranking. Magento has a reputation for being resource-intensive, and without the right server-side optimization, your Core Web Vitals will suffer. Google’s assessment of page experience—specifically Interaction to Next Paint (INP), Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—directly impacts how your site ranks.
The first step in addressing performance is your hosting environment. Shared hosting is rarely sufficient for a serious Magento build. You need a dedicated architecture that supports the latest technologies. This means running PHP 8.3 or newer and ensuring your database is optimized on MySQL 8. However, the real speed gains come from caching. Varnish Cache is essential for Adobe Commerce. It acts as a reverse proxy, serving static content instantly without hitting the backend server for every request. If Varnish is not configured correctly, or if your full-page cache is constantly being invalidated by a poorly coded extension, your server response times will skyrocket.
Beyond server caching, you must address the frontend. Historically, Magento 2 suffered from excessive JavaScript bloat. Modern builds in 2026 often utilize lightweight frontend solutions or headless architectures to bypass this. If you are still using the classic Luma theme, you are likely fighting an uphill battle against poor INP scores. Reducing the number of JavaScript files, utilizing HTTP/3 for multiplexing, and deferring non-essential scripts are mandatory steps.
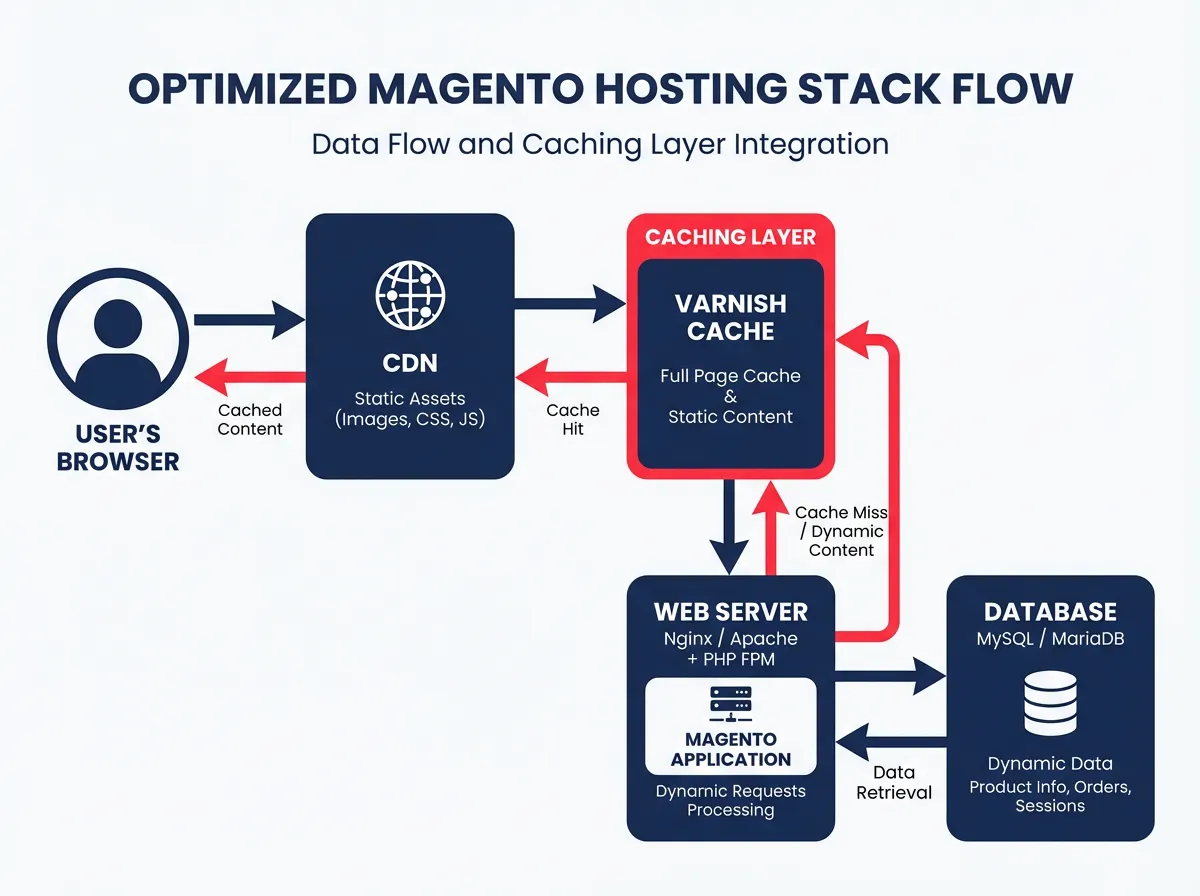
Another critical aspect of performance is image optimization. Ecommerce sites are naturally image-heavy. Serving legacy formats like JPG or PNG is no longer acceptable for a high-performance store. You should be utilizing Next-Gen formats like AVIF or WebP, which offer superior compression without quality loss. Adobe Commerce has native features to help with this, but they often require specific server modules to function correctly. Lazy loading should be applied to all images below the fold, ensuring the browser prioritizes the LCP element—usually the main product image—above everything else.
Mastering URL Structure and Rewrite Management
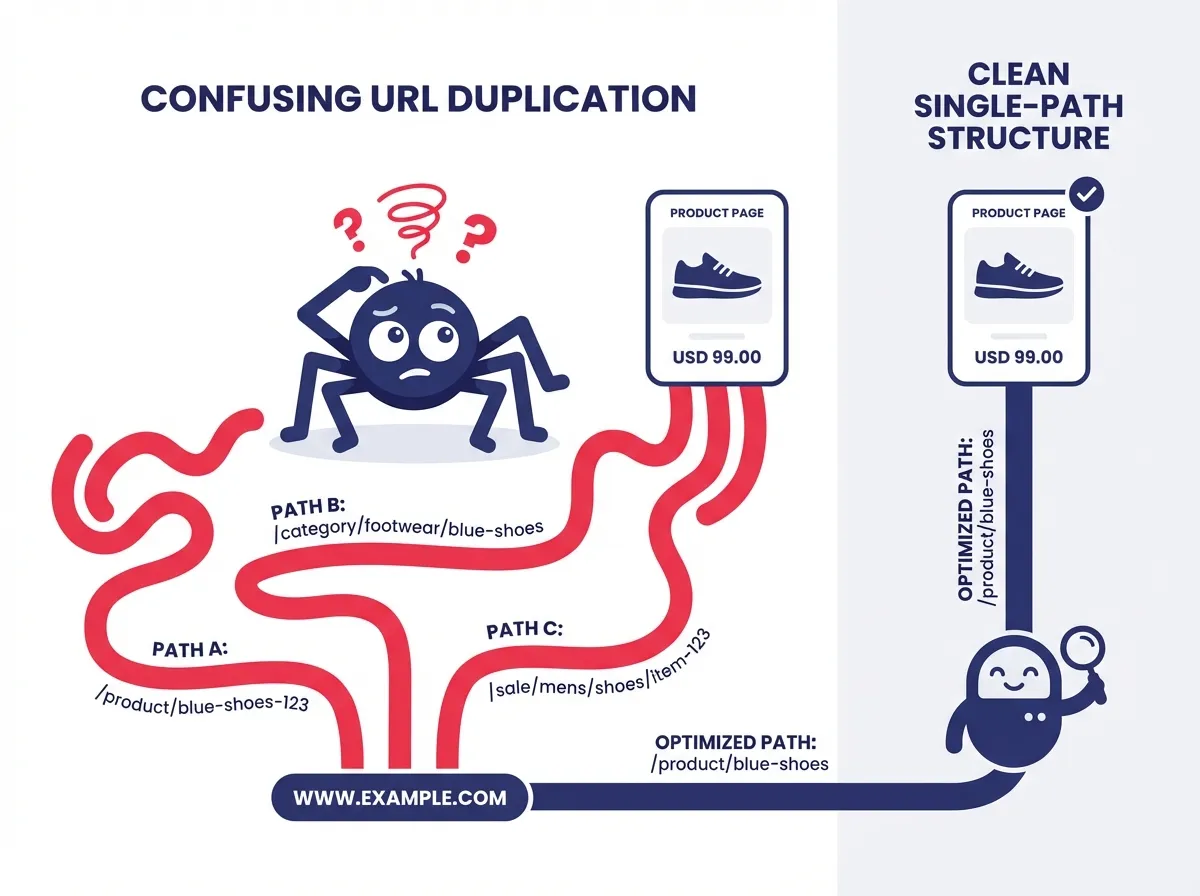
One of the most persistent issues in Magento SEO is the way the platform handles URLs. By default, Magento can generate multiple URLs for the same product. You might have a URL that includes the category path and another that is simply the product name at the root level. For example, you might see domain.com/men/jackets/winter-coat and domain.com/winter-coat serving the exact same content.
This creates a massive duplicate content issue. While canonical tags are a safety net, relying on them entirely is inefficient. It forces search engine bots to crawl multiple versions of a page only to be told to ignore all but one. This wastes your crawl budget, which is a finite resource, especially for stores with thousands of SKUs. The best practice in 2026 remains configuring your store to use top-level URLs for products effectively. This means disabling the “Use Categories Path for Product URLs” setting in the configuration menu.
However, simply changing a setting on a live site can be disastrous if you do not plan for redirects. When you change URL structures, you must ensure that 301 redirects are in place to pass authority from the old structure to the new one. Magento’s URL Rewrite tool is powerful but can become bloated. I have seen databases with millions of rows in the url_rewrite table, causing significant performance degradation.
You need to regularly perform an SEO Audit on this table. If you delete a product, Magento creates a redirect record. If you change a URL key, it creates another. Over time, these pile up. Truncating this table and regenerating rewrites is a common maintenance task, but it must be done with extreme caution to avoid creating 404 errors for legacy links that are still driving traffic.
The Challenge of Faceted Navigation
For any ecommerce store, faceted navigation (filtering by size, color, price, brand) is essential for user experience. For SEO, it is often a nightmare. Magento’s layered navigation generates unique URLs for every filter combination applied. If a user filters by “Blue,” “Size M,” and “Price $50-$100,” a new URL is created. With multiple attributes, this can result in millions of thin, low-value pages that search engines might try to index.
If Google gets trapped in your faceted navigation, it will waste resources crawling useless filter combinations instead of your core category and product pages. This dilution of link equity can tank your rankings. The solution involves a strict strategy using robots.txt directives, meta robots tags, and canonicalization.
In 2026, the standard approach is to decide exactly which filters have search demand. People search for “Red Nike Running Shoes,” so that combination should be indexable. People rarely search for “Shoes between $50 and $55,” so price filters should generally be blocked. You can control this within Magento’s XML sitemap settings and via robots.txt disallow rules for specific parameters.
Furthermore, AJAX filtering can help user experience but can obscure content from crawlers if not implemented with a fallback. Ensure that your implementation allows bots to see the links to the filtered pages you want indexed. If you are using a third-party extension for layered navigation—which most Magento stores do—check its settings meticulously. Many extensions default to “index everything,” which is dangerous. You want granular control over which attributes generate indexable pages and which apply a noindex, nofollow tag.
Product Page Optimization for Entities and AI
We have moved past the era where stuffing keywords into a product description was effective. Search engines now view products as entities with specific attributes. To rank for magento seo terms related to your products, you need to provide clear, structured data that machines can easily parse.
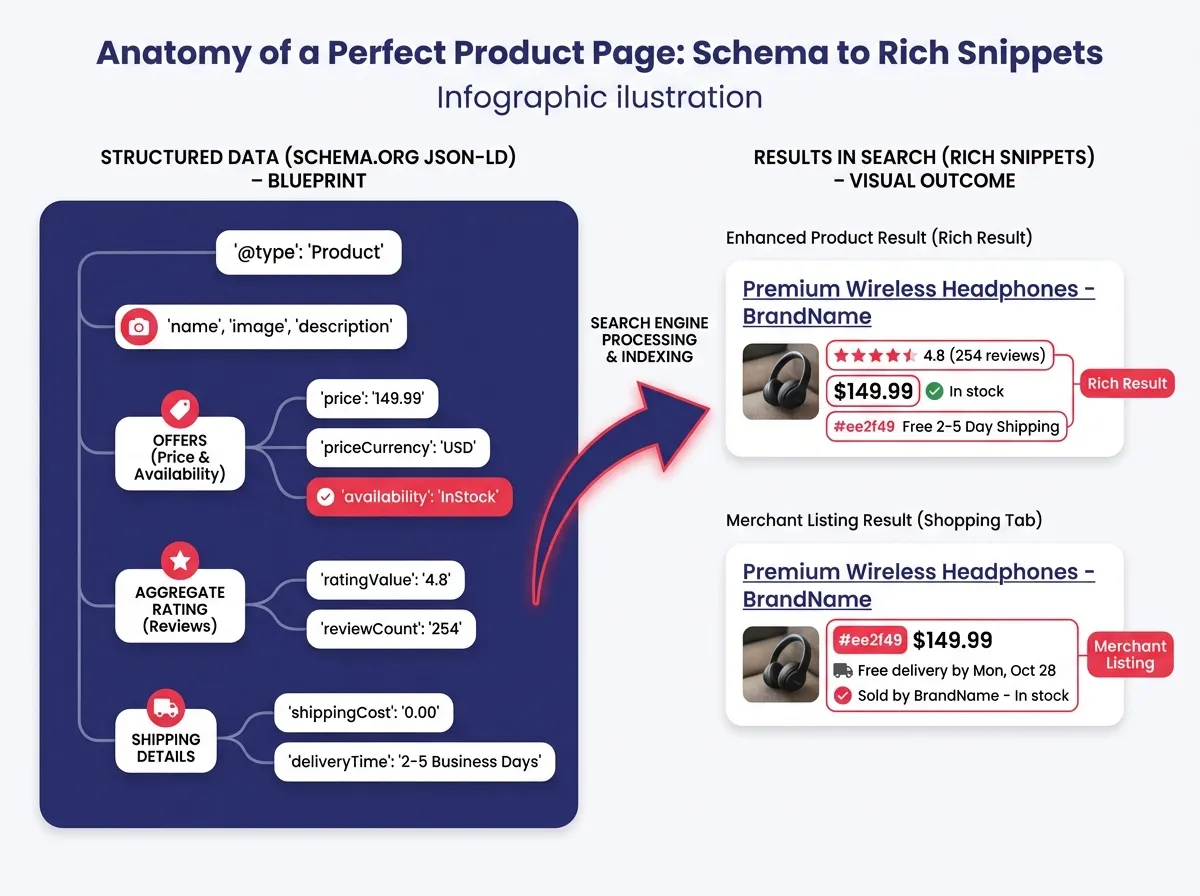
This brings us to Schema.org structured data. While Magento has some basic schema built-in, it is rarely detailed enough for modern requirements. You need comprehensive Product schema that includes gtin, mpn, brand, sku, offer, aggregateRating, and shippingDetails. In 2026, Merchant Center feeds and organic structured data are tightly coupled. If your on-page structured data contradicts your Merchant Center feed, you may lose visibility in Google Shopping features.
Beyond the code, the content on the page must be written for clarity. AI Overviews in search results summarize product pros and cons, specifications, and use cases. If your description is generic manufacturer text, the AI has nothing unique to work with. You need to expand your product descriptions to include unique selling points, material details, and care instructions.
Handling out-of-stock products is another area where strategy matters. Deleting a product page the moment it goes out of stock is a mistake. That page has accrued historical authority and might still be receiving traffic. Instead, keep the page live but clearly mark it as out of stock. Provide an option for users to sign up for a notification when it returns, or display related products prominently. If the product is discontinued permanently, 301 redirect it to the most relevant equivalent product, not just the parent category.
Addressing Duplicate Content with Canonicals
Duplicate content is not just a URL issue; it can happen with product data too. A common scenario in Magento is creating a “Simple” product for every variation (e.g., a shirt in Small, Medium, Large). Each of these simple products has its own page by default. However, you typically want the “Configurable” product (the main parent page) to be the one ranking.
If the simple products are indexable, they compete with each other and the parent page. The correct magento seo setup involves ensuring that simple products are not visible individually in the catalog unless there is a specific reason for them to be (like a specific color variant that has high search volume). Even then, you must be careful.
The canonical tag is your primary defense here. Every page on your site must have a self-referencing canonical tag if it is the primary version. For sorted category pages (e.g., “Sort by Price”), the canonical should point back to the default category URL. This tells Google that the sorted view is just a variation of the main list, not a new page deserving of independent ranking.
The Role of Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP)
Looking at the immediate future, we cannot ignore the rise of the Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP). As mentioned in industry discussions throughout late 2025 and early 2026, AI agents are beginning to perform shopping tasks on behalf of users. These agents do not “browse” visual websites; they consume data.
Adobe Commerce is well-positioned for this shift due to its API-first approach. However, enabling your store for agentic commerce requires more than just standard SEO. It requires your product data to be accessible via standardized protocols that AI agents can query. This means your attributes must be clean, your pricing logic must be exposed via API, and your inventory data must be real-time.
While this might sound like a developer’s task, it is deeply rooted in SEO. If an AI agent cannot “read” your product’s suitability for a user’s query because your data is unstructured, you lose the sale. Think of ACP optimization as the next layer of technical SEO. Just as we optimize HTML for crawlers, we must now optimize data structures for agents.
Managing the Crawl Budget
For large Magento stores with tens of thousands of products, crawl budget management is critical. Googlebot does not have infinite resources to spend on your site. If it spends time crawling low-value pages, it might miss your new product launches or updated content.
Log file analysis is the best way to understand how bots are interacting with your Magento store. By analyzing server logs, you can see exactly which URLs Googlebot is hitting. You might discover that the bot is stuck in a loop of calendar widgets, session ID URLs, or internal search result pages.
Internal search result pages are a common trap. By default, Magento might allow these to be crawled. However, Google explicitly advises against indexing search results pages. They add no unique value and create infinite crawl traps. Ensure your robots.txt file disallows /catalogsearch/ and that these pages have a noindex tag.
Additionally, use your XML sitemap strategically. Do not just dump every URL into the sitemap. Only include the URLs you specifically want to rank. Magento allows you to generate sitemaps automatically, but you should review the settings to exclude CMS pages that are not relevant for search (like “404 Not Found” or “Enable Cookies” pages) and ensure images are included for Google Images visibility.
International SEO and Store Views
One of Magento’s strongest features is its ability to handle multiple storefronts from a single backend. This is ideal for international expansion. However, international SEO requires precise implementation of hreflang tags. These tags tell search engines which version of a page to show to users based on their language and region.
In a Magento setup, you usually map different Store Views to different languages or regions. The challenge is ensuring that the hreflang tags are implemented correctly across all these views. If you have a US store and a UK store, both in English, you must use en-us and en-gb tags respectively. If you mess this up, Google might view the content as duplicate and pick only one to rank, effectively hiding your localized store from its target audience.
You must also consider currency and pricing. If your schema markup shows a price in USD on the UK store view because of a configuration error, you will confuse both the user and the search engine, potentially leading to a suspension in Google Merchant Center.
Building Topical Authority with Content
Finally, technical excellence allows you to compete, but content makes you win. Magento comes with a CMS, and the Page Builder introduced in recent versions is quite capable. However, many stores neglect their blog or Content Marketing strategy, viewing the platform purely as a transactional engine.
To rank for broad, informational queries, you need to build topical authority. This means creating content that answers the questions your customers have before they are ready to buy. If you sell specialized automotive parts, you should have detailed guides on installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
This content should be interlinked with your product pages. A blog post about “How to replace a timing belt” should link naturally to the timing belt category page. This passes authority from the informational content to the transactional pages. In 2026, where AI values “Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness” (E-E-A-T), showing that your brand is an expert in its niche is vital. Do not rely solely on third-party platforms like WordPress for your blog if it means the content lives on a subdomain. Subdirectories (e.g., domain.com/blog) are generally preferred for consolidating domain authority.
Optimizing a Magento store is a continuous process of refinement. The platform gives you the tools to control every aspect of your site’s presentation to search engines, but it requires a knowledgeable hand to guide it. By focusing on a solid technical foundation, controlling your crawl paths, and embracing the new reality of entity-based and agentic search, you can ensure your Adobe Commerce store thrives in the organic search results.